Metal Recovery Technology
Recovery of Precious Metals from Industrial Wastes
The key point of the technology
Most of the companies, generating fermentation wastes, throw their wastes into the
sea.
We invented high value sorbents out of the wastes to recover precious metals or
remove heavy metals.
The new invention, Bio-sorbent overwhelms IER(Ion Exchange Resin) in every way, and
it is also eco-friendly and highly efficient.
The entire recovery & removal cycle of Bio-sorbent is environmentally friendly, and
it enables us to overcome the shortcomings with the wet process.
he recycling of the wastes and the concrete securement of metal resource are the
beauty of the technology
The necessities of technical revolution
In various industry areas, using heavy metals and precious metals, called non-ferrous
metals, already became generalized.
The wastes containing these metals have been increasing continuously.
That is why there are growing needs to deal with these wastes more economically and
eco-friendly. Globally, it is strongly prohibited to throw fermentation wastes
into the sea; The regulation takes effect in 2016 in Korea. This technology will be
killing two birds with one stone under the circumstances.
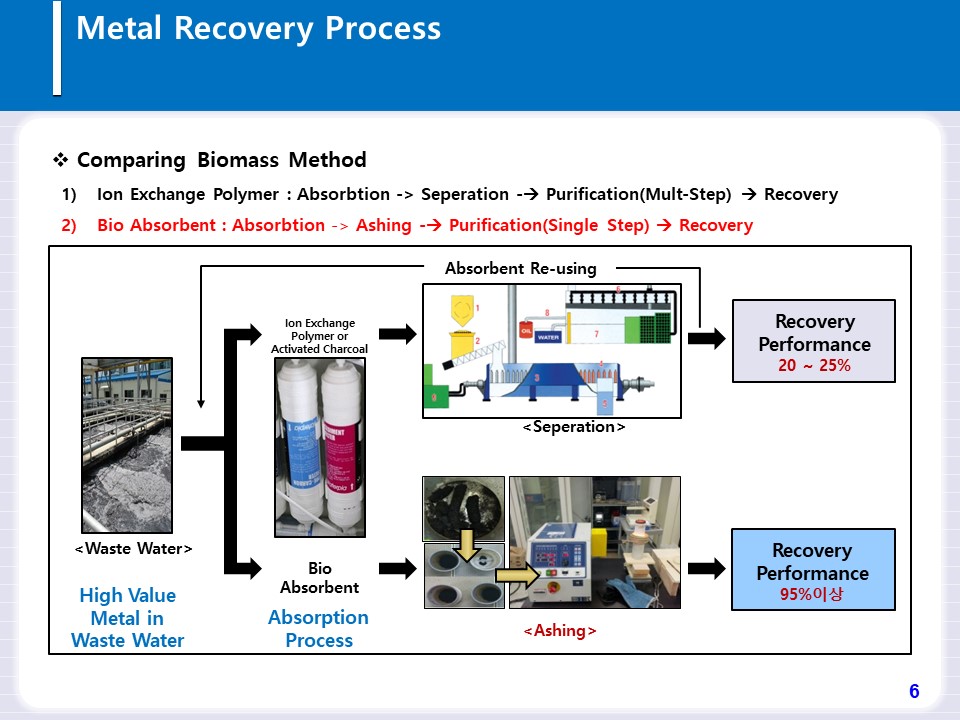
Where to use?
-
No.1

Recovery of precious metals from industrial wastes by means of using the highly efficient bio-sorbent.
-
No.2

Removal of heavy metals, dye wastewater, and ionic pollutants by means of using the highly efficient bio-sorbent.
-
No.3

Recycling fermentation wastes as high value sorbents.
Gas Reforming Technology
From fuel cells to hydrogen energy
What is the fuel cell?
It is an energy transforming technology from a chemical reaction between hydrogen and
oxygen to electric power without emitting pollutants.
Environmentally friendly and high-efficiency technology.
From hydrogen on the anode and oxygen on the cathode, it generates energy as a
reverse reaction of electrolysis. The type of the energies are electricity and
heat.
The main source comes from town gas (LNG, LPG), Biogas and so on, and transform them
to hydrogen. Since then, the technology is not limited by geographical
factors.
It can be used not only for electricity, but for also hot-water supply and heating.
The reasons to become the next generation energy
-
High-efficiency
• The technology directly transforms fuel cells into energy.
It shows 10~20% higher efficiency, compared to the existing method.• The fuel energy technology reaches 80% of energy efficiency as 40% of electricity and 40% of heat energy.
It is able to use both energy types simultaneously -
Green generating process
• Hydrogen and oxygen as the raw materials are harmless,
and the transformed material, water is also innocuous.• Carbon dioxide, emitted during the transforming process,
is less than a thermal power generation.
The reasons to become the next generation energy
-
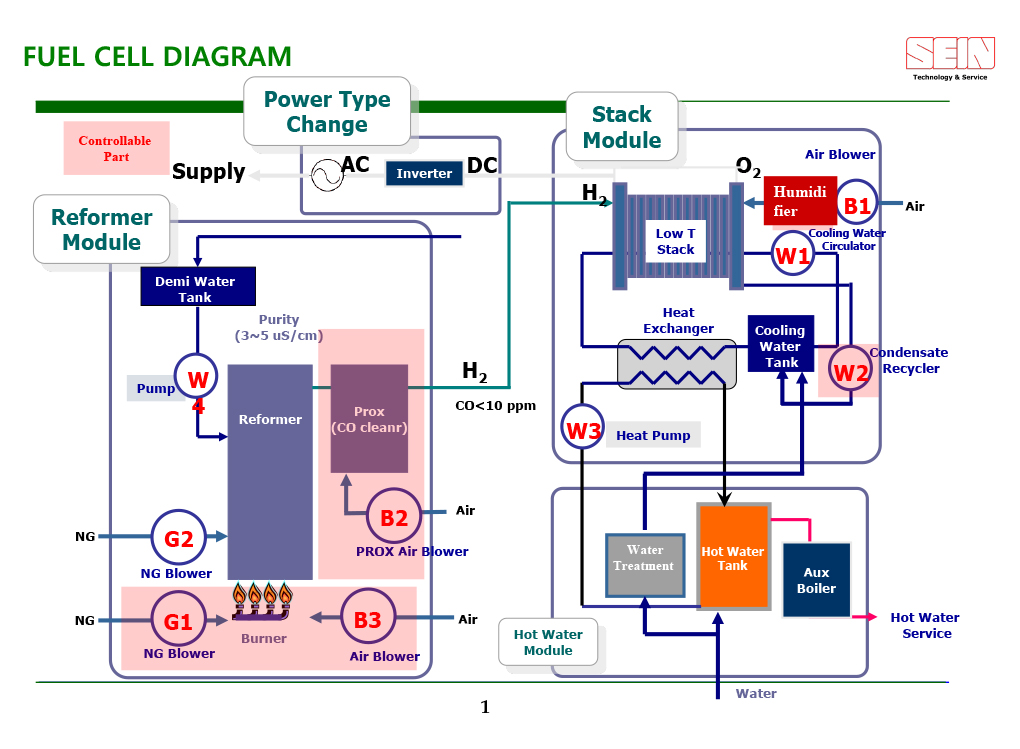
Reformer
The device catalytically reacts fossil fuels, and transforms them into reformed gas. The gas is injected into fuel cells.
-
Stack
The device generates energy by an electrochemical method between hydrogen from Reformer and Oxygen
-
Electricity inverter
The device changes direct current, coming from fuel cells, to inter current.
Reformer for hydrogen supply
-
Partial Oxidation (POX)
The device catalytically reacts fossil fuels, and transforms them into reformed gas. The gas is injected into fuel cells.
-
Steam Reforming (SR)
The power generation method by natural gas and steam is the most economical means, since the hydrogen production efficiency is higher than 70%.
-
Autothermal Reforming (ATR)
Partial Oxidation (POX) and Steam Reforming (SR) occur at the same time. Therefore, this system can be operated without heat supply from outside.
Reforming System Diagram
-
Desulfurizer
Sulfur in town gas should be eliminated, since reforming catalysts can be contaminated by sulfur, and it can cause deactivation.
-
Primary Process
Separation of fuels in the hydro carbon line for reforming process. The fuels are separated into Hydrogen and Carbon.
-
Selective Oxidizer
Decreasing carbon monoxide to several ppm by means of using air to supply reformed gas into stacks.
-
Steam Generator
Heating water to supply steam for the reforming process.